Updated February 2023
On this page
Magnesite properties and uses
Magnesite (MgCO3) is a magnesium carbonate mineral that is the source of two-thirds of the world's magnesia (MgO). Magnesium (Mg) is a versatile element with a variety of applications in modern society.
Magnesium forms a strong, lightweight metal alloy, which uses include:
- aircraft and automotive components
- laptops, televisions, mobile phones
- portable power tools
- bicycles and other sporting equipment.
Caustic calcine magnesia (CCM) is a highly reactive form of magnesium oxide that is created by calcining magnesite at temperatures >1000 °C. CCM is used for:
- animal feeds and fertilisers
- magnesia cements, flooring compounds and other building materials
- water and effluent treatment, and flue gas desulphurisation
- metallurgical flux
- flame retardants
- heat resistant linings.
Magnesite in South Australia
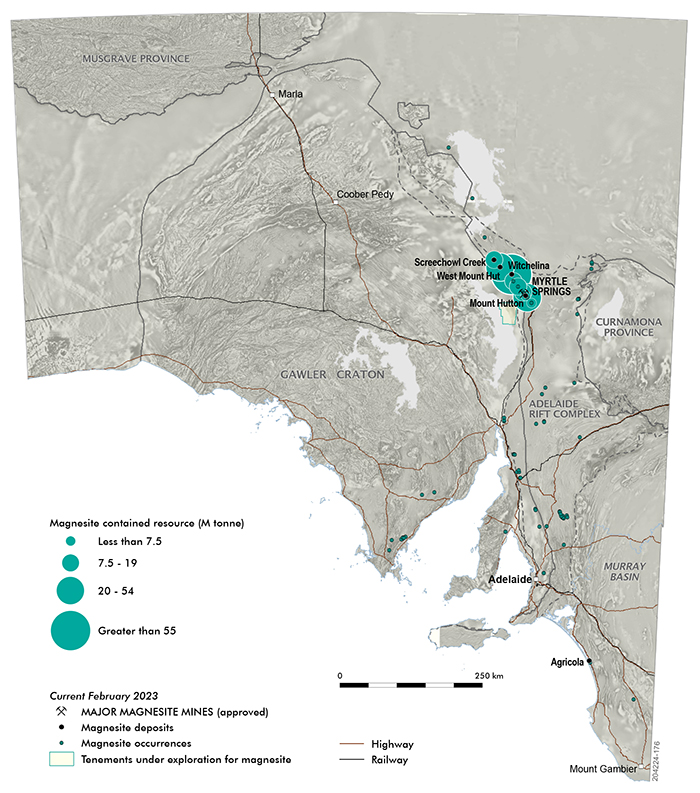
The majority of South Australia’s known magnesite deposits are clustered in the northern Flinders Ranges. However, there are also known deposits in the Coorong region in the state’s southeast, and small surface deposits on the Eyre Peninsula.

Magnesite at Mount Hutton.
Northern Flinders Ranges
Numerous sedimentary magnesite deposits occur as interbeds within the Skillogalee Dolomite of the Adelaide Rift Complex. The magnesite was deposited as a chemical precipitate in shallow, marginal marine lagoons and mudflats, and occurs predominantly as cryptocrystalline particles 1–5 µm in size. Much was reworked by storm and tidal action into intraformational conglomerates thinly interbedded with dolomite. The main magnesite deposits in this region include Myrtle Springs, Mount Hutton, Termination Hill, Witchelina, Mount Playfair, Pug Hill and Camel Flat.
The northern Flinders Ranges also contains replacement deposits of magnesite. Irregular bodies of coarsely crystalline sparry magnesite have been formed by metasomatic replacement of dolomite within the Balcanoona Formation, near Balcanoona and in the Mount Fitton–Mount Livingston area.
Coorong region
Fine dolomitic magnesite sediment has accumulated on the bed of playa lakes within the Quaternary Bridgewater Formation, adjacent to the Coorong in the State's southeast. The Agricola Mine is one example of this deposit type in this area.
Eyre Peninsula
Small deposits of surficial magnesite have developed on magnesium-rich dolomite of the Hutchison Group on Eyre Peninsula. Although some nodules are relatively pure (94–97% MgCO3), the deposits are thin and discontinuous.
Major mines
South Australia currently has two operating magnesite mines:
- Myrtle Springs (Magnesium Developments) – Total magnesite resource of 11 Mt at 42.9% MgO.
- Agricola (Agricola Mining) – Total resource unknown.
Magnesite deposits
Numerous undeveloped magnesite deposits also exist in South Australia:
- Witchelina – Total magnesite resource of 86.7 Mt at 40% MgO.
- Mount Hutton South – Total magnesite resource of 125 Mt at 42.9% MgO.
- Mount Hutton Central – Total magnesite resource of 17.5 Mt at 40.1 % MgO.
- Pug Hill – Total magnesite resource of 20 Mt at 42.7% MgO.
- Mount Playfair – Total magnesite resource of 18.7 Mt at 42.5% MgO.
- Camel Flat – Inferred magnesite resource of 13 Mt 42% MgO.
Additional reading
McCallum WS 1990. Magnesite deposits in South Australia. In: FE Hughes (Ed.), Geology of the mineral deposits of Australia and Papua New Guinea. Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. Monograph Series 14:1151–1154.